react学习(九) React 新的生命周期
我们在之前已经学习过 react 生命周期,但是在 16 版本中 will 类的生命周期进行了废除,虽然依然可以用,但是需要加上 UNSAFE 开头,表示是不安全的。
-
React16废弃的生命周期有3个will:componentwillMountcomponentwillReceivePropscomponentwillUpdate
废弃的原因,是在 React16 的 Fiber 架构中,可以中间进行暂停重启操作,调和过程会多次执行 will 周期,不再是一次执行,失去了原有的意义。此外,多次执行,在周期中如果有 setState 或 dom 操作,会触发多次重绘,影响性能,也会导致数据错乱. 因而会有 UNSAFE 开头。
更改的生命周期主要发生在更新时
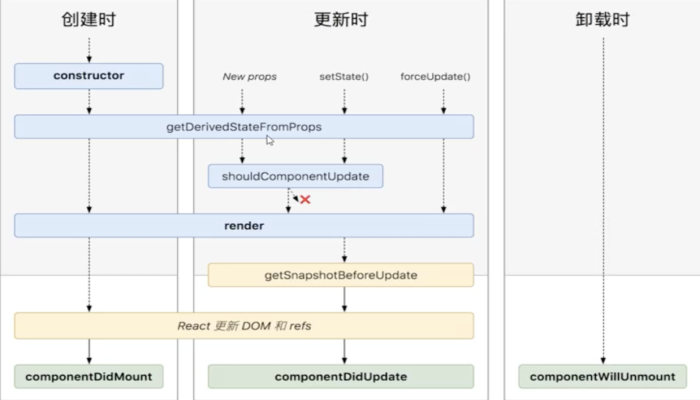
该生命周期是从父获取数据时使用的,返回一个新状态和页面当前状态组合,如下示例:
// src/index.js
class Child extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0
}
// 静态方法
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, nextState) {
return {
count: nextProps.count * 2
}
}
render() {
return <div>{this.state.count}</div>;
}
}
由上可知,函数执行应该在渲染之前执行,这样才能保证数据同步渲染,由上面生命周期图可知,props 和 state 和 forceupdate 都会触发该生命周期,所以我们在通用方法 forceUpdate 中实现如下:
// src/component.js
forceUpdate() {
let oldRenderVdom = this.oldRenderVdom;
let oldDOM = findDOM(oldRenderVdom);
// 渲染前触发
if (this.constructor.getDerivedStateFromProps) {
const newState = this.constructor.getDerivedStateFromProps(this.props, this.state)
if (newState) {
this.state = {
...this.state,
...newState
}
}
}
...getSnapshotBeforeUpdate这里为什么使用静态方法呢?可能因为在
componentwillReceiveProps中会有人乱用setState,导致形成死循环,所以改成了静态方法
从字面理解在更新前获取当前 dom 结构的快照,拿到更新前页面的各种状态。例如你在渲染前浏览器滚动条 scrollTop,更新后会变化,你就可以记住当前状态进行计算。
值得注意,getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 方法可以返回一个对象,在 componentDidUpdate 第三个参数可以获取。
示例如下:
class ScrollList extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
messages: []
}
this.container = React.createRef()
}
componentDidMount() {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
this.addMessage()
}, 1000)
}
componentwillUnmount() {
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
addMessage = () => {
this.setState({
messages: [`${this.state.messages.length}`,...this.state.messages, ]
})
}
// 返回值给到 didupdate
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
// 记住当前滚动条位置
return {
prevScrollTop: this.container.current.scrollTop,
prevScrollHeight: this.container.current.scrollHeight
}
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevstate, {prevScrollTop ,prevScrollHeight}) {
this.container.current.scrollTop = prevScrollTop + (this.container.current.scrollHeight - prevScrollHeight)
}
render() {
const style = {
height: '100px',
width: '200px',
border: '1px solid red',
overflow: 'auto'
}
return <div style={style} ref={this.container}>
{this.state.messages.map(msg => {
return <div key={msg}>{msg}</div>
})}
</div>
}
}既然也是在渲染前触发该方法,同样我们在 forceUpdate 中的 render 前实现:
forceUpdate() {
...
// 更新前调用
const snapShot = this.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
let neWrenderVdom = this.render();
...
if (this.componentDidUpdate) {
this.componentDidUpdate(this.props, this.state, snapShot);// 第三个参数
}
}该生命周期具体使用情况大家根据自己的实际情况使用,文中的小示例仅供大家理解使用情况。
本节概念不是很多,主要是了解了 react 为了 fiber 提出了两个新生命周期。下一小节我们学习下 react 中的 context 概念。
原文地址:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2012887